Basic Of Options Trading
Options trading is a fascinating and potentially lucrative way to participate in the financial markets. It’s crucial to understand the basics of options trading to make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
In this blog, we’ll cover the fundamental concepts of options trading to help you get started on your trading journey.
What Is Options Trading ?
Option trading is a type of trading strategy where investors have the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a certain time frame, but these contracts do not provide any obligation to buy or sell. These contracts are called options.
How Options Trading Works?
Options trading involves buying and selling contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price (called the strike price) on or before a certain date (called the expiration date).
Types of Options :
There are two main types of options: Call options and Put options

Call Option:
Call Options give the buyer the right to buy the Underlying Asset at the Strike Price before the Expiration Date. Traders typically buy call options when they expect the price of the underlying asset may rise.
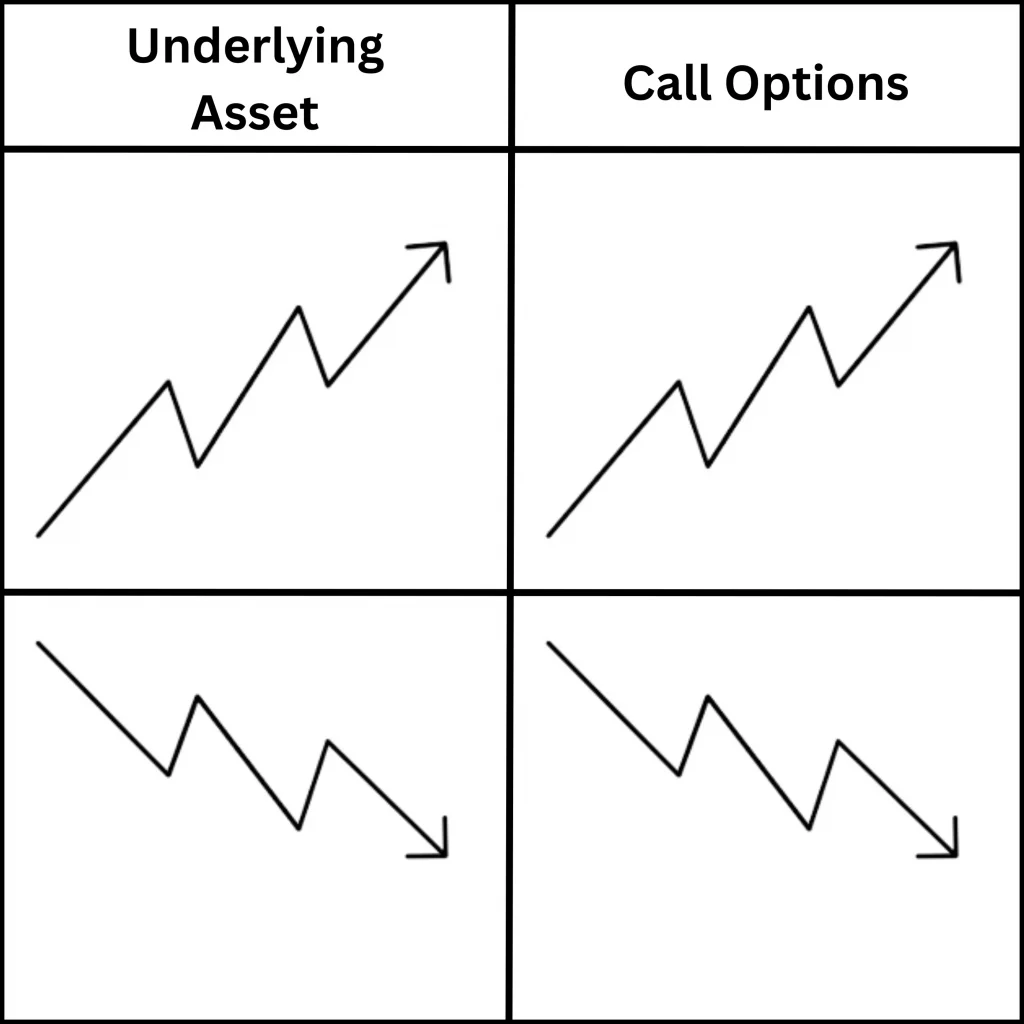
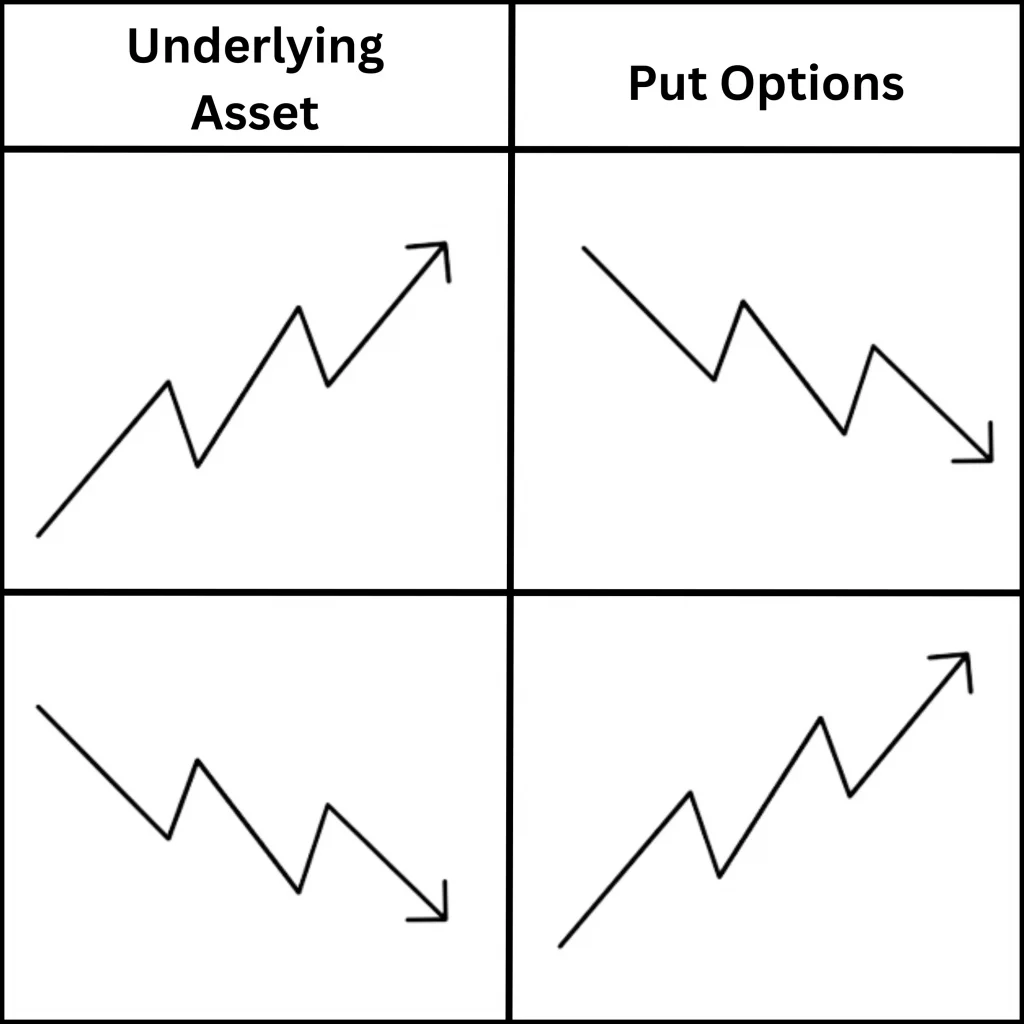
Put Option:
Put options give the buyer the right to sell the Underlying Asset at the strike price before the expiration date. Traders usually buy put options when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset may fall.
Terminology of Options Trading:
Underlying Asset :
The Underlying Asset is the financial instrument or security upon which a derivative contract is based. In options trading, the Underlying Asset can be a stock, index, commodity, currency pair, or even another derivative instrument.
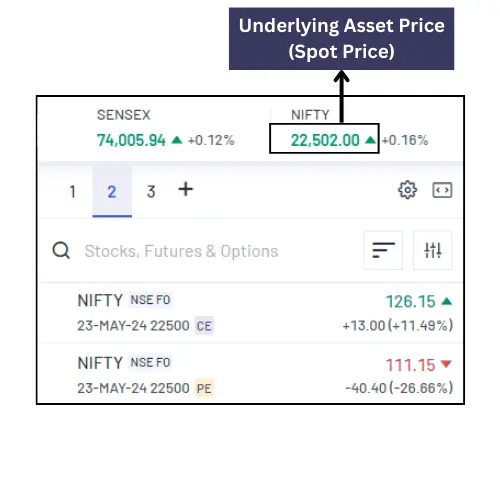
Underlying Asset Price (Spot Price):
Underlying Asset Price and Spot Price are the same, Both of them indicate the current market price where an asset can be bought or sold.
For example, the Underlying Asset price of an Index option is the spot price of the Index.
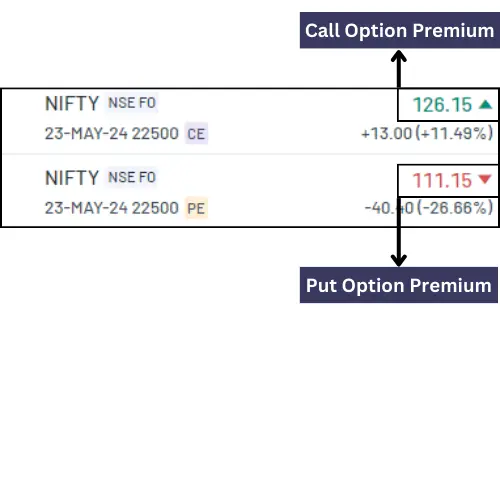
Option Premium:
An option premium is the current market price of an option contract. It represents the income received by the seller of an option contract from another party.
However, there is a difference between Call Option Premium and Put Option Premium.
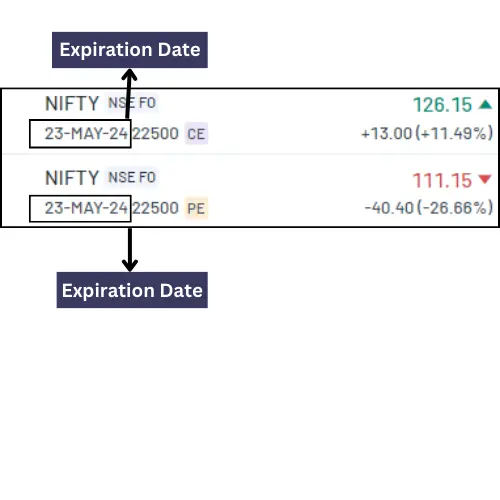
Expiration Date:
Expiration date is the date on which the value of an option contract becomes invalid and then the contract ceases to exist.
After the Expiration Date, the Option becomes worthless along with its all associated rights.
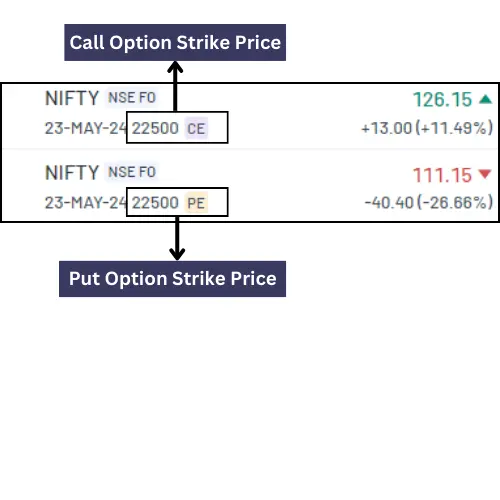
Strike Price:
The strike price, also known as the exercise price, is the predetermined price at which the holder of an options contract can buy or sell the underlying asset.
Key Points:
- In the case of a call option: The strike price is the price at which the option holder can buy the underlying asset.
- In the case of a Put option: The strike price is the price at which the option holder can sell the underlying asset.
- The strike price is set when the options contract is created and remains fixed throughout the life of the option.
- Profitability of an option depends on the relationship between the strike price and the market price of the underlying asset.
▪ Remember that options trading involves risks, and there’s no guarantee of profits. Take your time to learn and practice, and gradually build your skills and confidence as a trader.
FAQs
You can get started trading options by opening an Demat account, choosing to buy or sell puts or calls, and choosing an appropriate strike price and timeframe.
Options trading can be risky, sometimes riskier than trading stocks. But if you learn about it, you can also find ways to reduce risk.
Earning Rs 1000 per day in the share market might seem ambitious, but it is achievable with the right strategies, knowledge, and discipline.
To become successful, options traders must practise with discipline.
Options prices are influenced by factors such as the price of the underlying asset, the strike price, time to expiration, volatility, and interest rates.
Starting trading on your own can become complicated at times, and you would need a mentor to walk you through the investment process.
এই তথ্য শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষামূলক উদ্দেশ্যে প্রদান করা হয়েছে। একে কোনোভাবেই Investment Advice বা Recommendation হিসেবে গণ্য করা উচিত নয়। আমরা একটি SEBI-registered Organization, এবং আমাদের মূল লক্ষ্য হলো বিনিয়োগ সম্পর্কিত Concepts-এর সাধারণ জ্ঞান ও বোঝাপড়া বৃদ্ধি করা।
প্রত্যেক পাঠক/দর্শককে অনুরোধ করা হচ্ছে, যেকোনো Investment Decision নেওয়ার আগে নিজস্ব Research এবং Analysis করুন। Investment সর্বদা হওয়া উচিত ব্যক্তিগত Conviction-এর ভিত্তিতে, অন্যের মতামত থেকে নয়। অতএব, প্রদত্ত তথ্যের ওপর ভিত্তি করে নেওয়া কোনো ধরনের Investment Decision-এর জন্য আমরা কোনোভাবেই Liability বা Responsibility গ্রহণ করি না।



Leave a Reply