The term “Union Budget” refers to the annual financial statement of the government of India. It is also known as the General Budget.
Under Article 112 of the Constitution, a statement of estimated receipts and expenditure of the Government of India has to be laid before Parliament in respect of every financial year which runs from 1st April to 31st March.
This statement titled as “Annual Financial Statement” is the main Budget document.
- Consolidated Fund,
- Contingency Fund and
- Public Account.
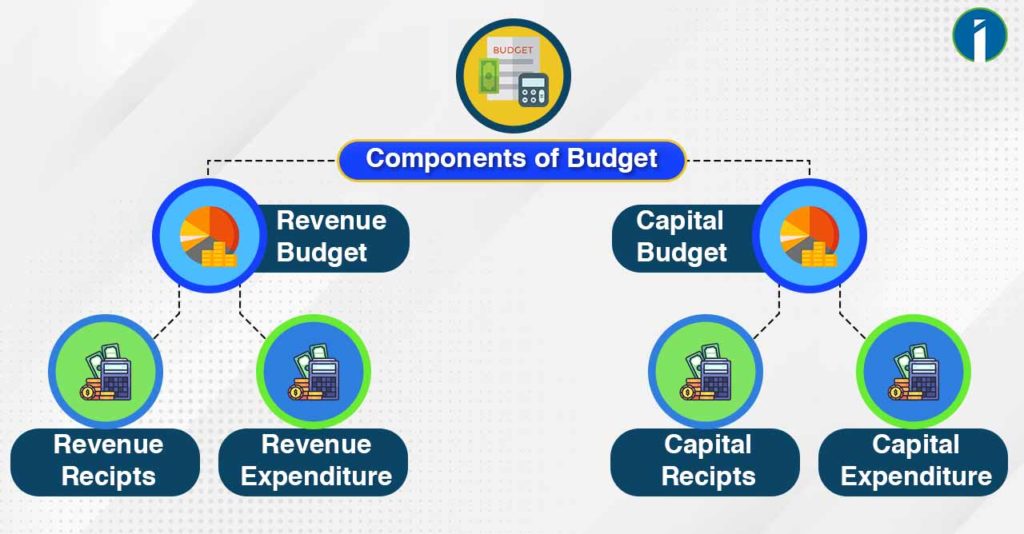
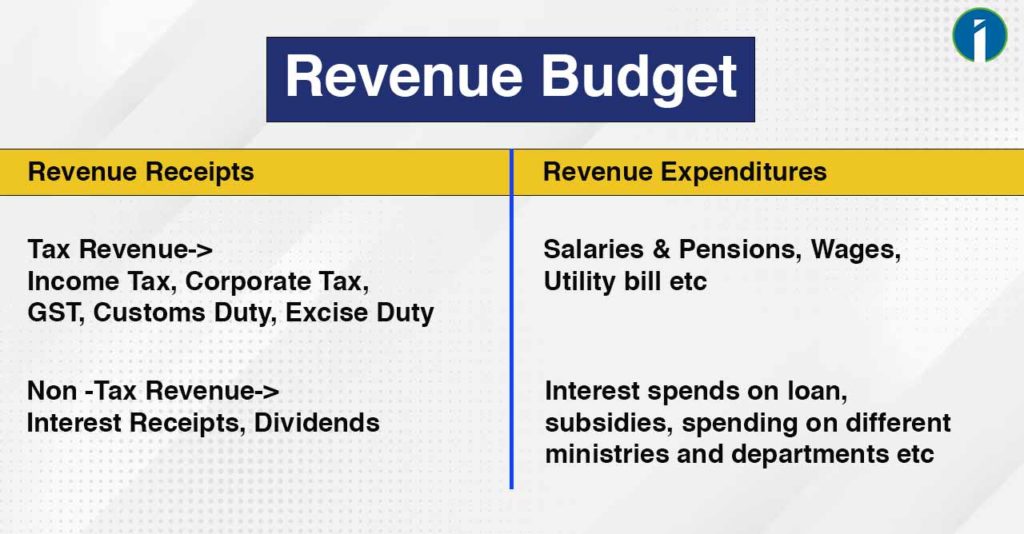
- Revenue Budget
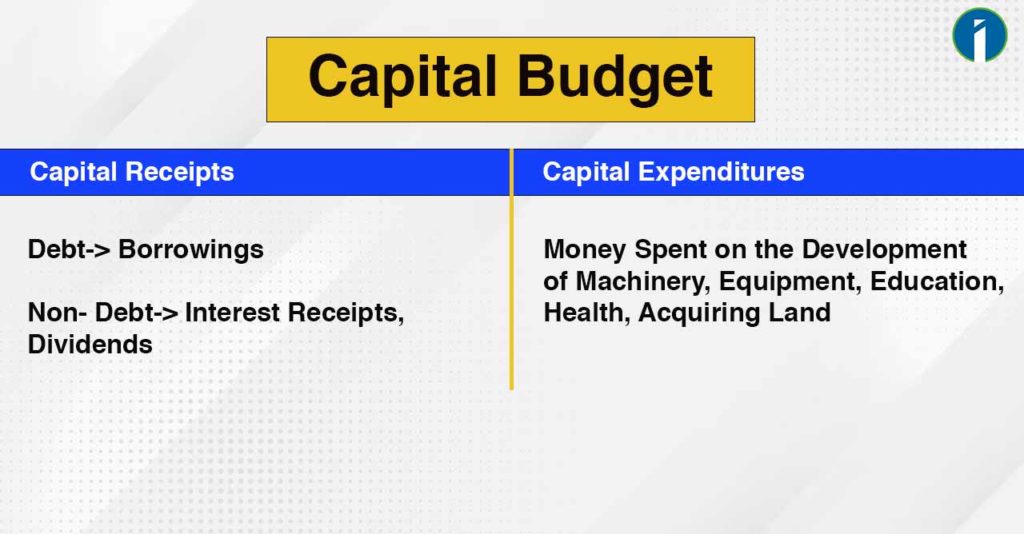
- Capital Budget
Budget policy refers to government attempts to run a budget in equity or in surplus. The aim is to reduce the public debt.
It is not the same as a fiscal policy, which deals with the fiscal stimulus to the economy, the re-partition of taxes and the generosity of allowances. It is the policy which governments adopt while formulating budget.
Budgetary policy is determined by the government’s expenditures and revenues plans and expected national and international economic developments over the next four years.
The government sets the expenditure for its entire term of office (four years) in real terms when it takes office. The expenditure relates to three sectors: central government (the ministries), social security and care.
The greater part of central government expenditure is financed from taxes. Social security and care expenditure is funded chiefly from contributions (e.g. for unemployment insurance and exceptional medical expenses insurance).
- taxes (main source of revenue)
- natural gas revenue
- income/profits from state holdings in private enterprises;
- fines
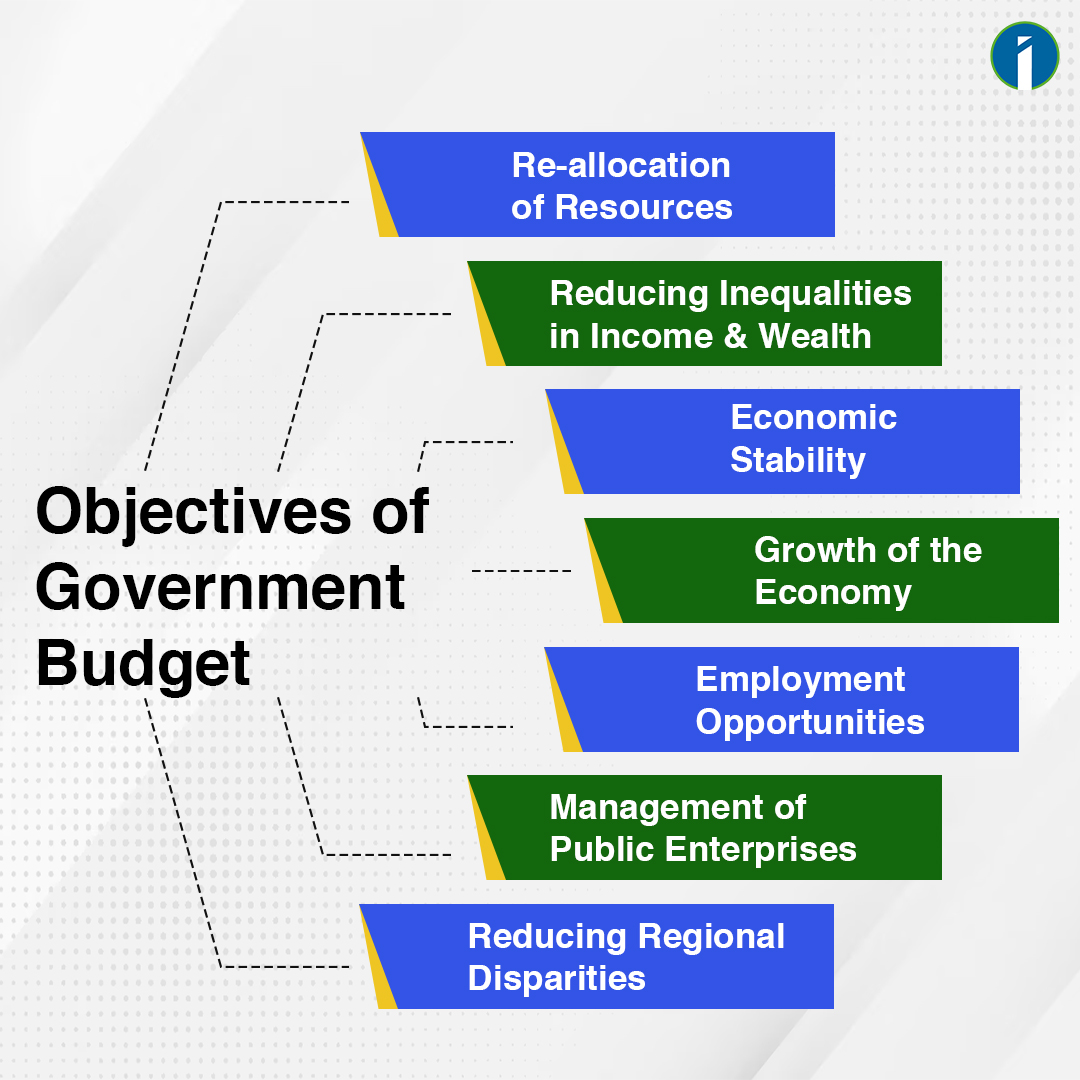
Financial stability is facilitated by a budget. Every government needs budgets to function. They dictate how public funds are allocated between numerous sectors. Simply, the budget is like a road-map that guides the government on how to allocate its resources to meet its objectives.
- Balanced Budget
- Surplus Budget
- Deficit Budget
A balanced budget means projected revenue matches expected expenses. Simply put, a balanced budget emerges when the government’s projected spending matches its expected income in a specific financial year. Many classical economists support this view, emphasizing the idea of “living within means.” They believe that the government’s expenses should mirror its revenue.
This budgetary approach aims to strike harmony in the economy, promote fiscal discipline, prevent excessive borrowing, and reduce the burden of interest payments. However, during economic depression or deflation, a balanced budget might not guarantee economic stability. In theory, it is simple to strike a balance between projected expenses and income, but in actual practice, this is challenging to do.
Merits of a Balanced Budget
- Ensures economic stability, if implemented successfully.
- Ensures that the government refrains from imprudent expenditures.
Demerits of a Balanced Budget
- Unviable at times of recession and does not offer any solution to problems such as unemployment.
- Inapplicable in less developed countries as it limits the scope of economic growth.
- Restricts the government from spending on public welfare.
In this budget, estimated government revenues are higher than estimated government expenditures. It serves to reduce the state’s public debt or increase its savings. At times of inflation, a government can choose this budget type to reduce aggregate demand and achieve economic stability. It highlights a country’s approach to budget management, allocating resources prudently, and investing in future projects without borrowing.
Features:
- Acts as a cushion during economic downturns.
- Can help in paying off existing debts.
The estimated government revenue in this budget is below estimated government spending. the deficit budget does have its benefits – it can help stimulate economic growth, promote investments in infrastructure, or address critical needs.
For nations like India, striving for growth, such a financial budget proves beneficial. By increasing spending, a government boosts demand, thus reviving economic growth. Another important aspect of this budget lies in job creation. Consequently, demand for goods and services soars.
Merits of a Deficit Budget
- Helps in addressing public concerns such as unemployment at times of economic recession.
- Enables the government to spend on public welfare.
Demerits of a Deficit Budget
- Can encourage imprudent expenditures by the government.
- Increases burden on the government by accumulating debts.
- Fiscal Deficit is the difference between total expenditure and revenue receipts, recovery of loans & advances and other non-debt capital receipts.
- Revenue Deficit is the difference between Revenue expenditure and Revenue Receipts.
- Primary Deficit is Fiscal Deficit net of ‘Interest Payments and Debt Servicing’ under Revenue Component.
- Budget Deficit is the difference between total expenditure and total receipts and has to be zero in the absence of monetization. Governments have no access to the monetization route and as such Budget Deficit in their case ought to be zero.
- Miscellaneous Capital Receipts (MCR) are treated as Non-Debt Capital Receipts.
- Finance Bill consists the Government’s proposals for the imposition of new taxes, modification of the existing tax structure or continuance of the existing tax structure beyond the period approved by the legislature.
The Union executive consists of the President, the Vice-President, and the Council of Ministers with the Prime Minister as the head to aid and advise the President.
The three branches of the union government are charged with different responsibilities, but the constitution also provides a fair degree of interdependence.
এই তথ্য শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষামূলক উদ্দেশ্যে প্রদান করা হয়েছে। একে কোনোভাবেই Investment Advice বা Recommendation হিসেবে গণ্য করা উচিত নয়। আমরা একটি SEBI-registered Organization, এবং আমাদের মূল লক্ষ্য হলো বিনিয়োগ সম্পর্কিত Concepts-এর সাধারণ জ্ঞান ও বোঝাপড়া বৃদ্ধি করা।
প্রত্যেক পাঠক/দর্শককে অনুরোধ করা হচ্ছে, যেকোনো Investment Decision নেওয়ার আগে নিজস্ব Research এবং Analysis করুন। Investment সর্বদা হওয়া উচিত ব্যক্তিগত Conviction-এর ভিত্তিতে, অন্যের মতামত থেকে নয়। অতএব, প্রদত্ত তথ্যের ওপর ভিত্তি করে নেওয়া কোনো ধরনের Investment Decision-এর জন্য আমরা কোনোভাবেই Liability বা Responsibility গ্রহণ করি না।



Thank You For The Updates….