Commodity exchanges are organized marketplaces where futures trade occurs through a centralized mechanism, fostering competitive trading among buyers and sellers.
Understanding the Role of Commodity Exchanges
1. Price Discovery
- True Market Value: Exchanges match supply with demand to determine the accurate price of commodities.
- Transparency: This process prevents market manipulation, ensuring fair trading for all participants.
2. Risk Management
- Price Protection: Futures and options contracts help traders lock in prices for future transactions.
- Reducing Uncertainty: These tools lower market volatility and minimize price change risks.
3. Quality Assurance
- Setting Standards: Exchanges define quality and quantity standards for commodities.
- Ensuring Consistency: These standards reduce delivery disputes and ensure uniformity.
4. Market Development
- Encouraging Competition: Exchanges drive growth and innovation by fostering competition among market participants.
- Creating Opportunities: They bring together buyers, sellers, and investors, enabling value addition and wealth creation.
Three-Tier Regulatory System
- Ministry Of Consumer Affairs: Responsible for monitoring prices, consumer movement, controlling statutory bodies like BIS, internal and inter-state trade, and controlling futures trading under relevant acts.
- Department for Food and Public Distribution: Ensures food security through efficient procurement and distribution, maintains food stocks, and supports farmers via Minimum Support Price. Manages PDS, Antyodaya Anna Yojna, grain banks, and sugar sector regulations, including export/import of food grains, sugar, and edible oils.
- Forward Market Commission (FMC): Advises the government on market regulations, monitors forward markets, publishes trading information, and inspects accounts of recognized associations.
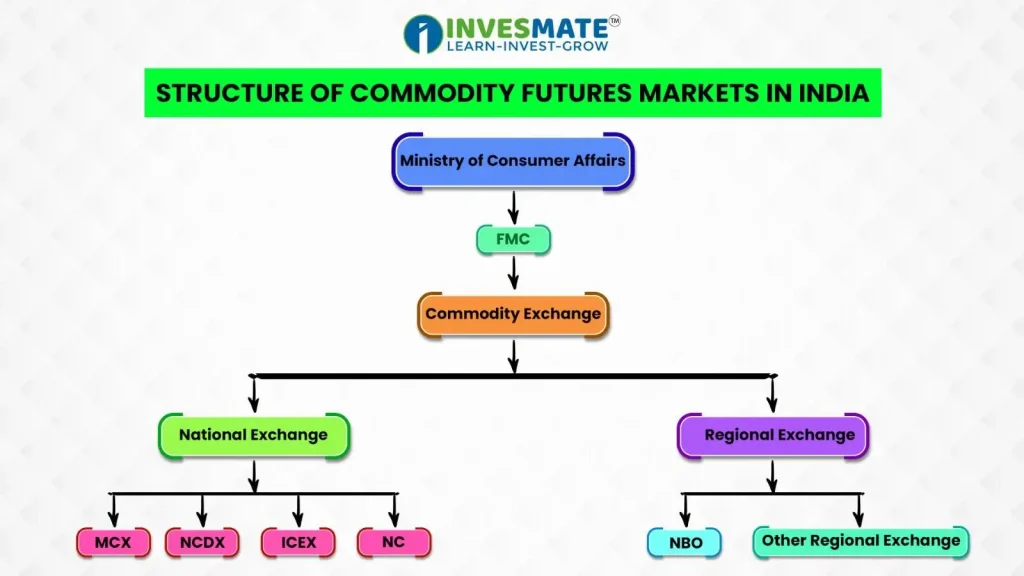
Participants/Players in Commodity Markets
Hedgers
Hedgers reduce the risk of price fluctuations by using futures contracts to lock in prices for commodities.
Role:
Protect against price volatility.
Secure stable costs for commodities.
Ensure consistent supply and pricing.
Examples:
ITC Ltd hedging against potential price drops in crops.
ONGC securing prices for future oil production.
Tata Steel locking in costs for raw materials like metals.
Speculators
Speculators aim to profit from price movements of commodities without having an underlying interest in the physical commodities.
Role:
Provide liquidity to the markets.
Aid in price discovery.
Assume the risks that hedgers want to avoid.
Examples:
Individual traders predicting commodity price movements.
Reliance Mutual Fund taking positions in commodity futures.
Edelweiss Financial Services engaging in short-term trades.
Arbitrageurs
Arbitrageurs profit from price discrepancies by buying and selling identical or equivalent commodities in different markets simultaneously.
Role:
Ensure price uniformity across different markets.
Enhance market efficiency.
Help in balancing supply and demand.
Examples:
Zerodha traders exploiting price differences between two exchanges.
Adani Enterprises using differences in spot and futures prices.
International traders taking advantage of price variances between countries.
Read Our Blog : Market Order Vs Limit Order
Conclusion
These components work together to ensure the efficient functioning of commodity markets, facilitating secure and transparent trading, and minimizing risks for participants.
FAQs
Three of the most commonly traded commodities include oil, gold, and base metals.
The market operates Monday to Friday in two sessions: morning (9:00 A.M. – 5:00 P.M.) and evening (05:00 P.M. – 11:30 P.M./11:55 P.M.)
Hedgers are usually Manufacturing and Producers, who use the Commodity Future Market to hedge against risk.
Since September 28, 2015, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has regulated the commodity derivatives market in India. The former Forward Markets Commission governed the commodity futures market prior to September 28, 2015. (FMC).
Traders make money by buying commodities or commodity derivatives for a certain price and then subsequently selling them for a higher price.
এই তথ্য শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষামূলক উদ্দেশ্যে প্রদান করা হয়েছে। একে কোনোভাবেই Investment Advice বা Recommendation হিসেবে গণ্য করা উচিত নয়। আমরা একটি SEBI-registered Organization, এবং আমাদের মূল লক্ষ্য হলো বিনিয়োগ সম্পর্কিত Concepts-এর সাধারণ জ্ঞান ও বোঝাপড়া বৃদ্ধি করা।
প্রত্যেক পাঠক/দর্শককে অনুরোধ করা হচ্ছে, যেকোনো Investment Decision নেওয়ার আগে নিজস্ব Research এবং Analysis করুন। Investment সর্বদা হওয়া উচিত ব্যক্তিগত Conviction-এর ভিত্তিতে, অন্যের মতামত থেকে নয়। অতএব, প্রদত্ত তথ্যের ওপর ভিত্তি করে নেওয়া কোনো ধরনের Investment Decision-এর জন্য আমরা কোনোভাবেই Liability বা Responsibility গ্রহণ করি না।



Leave a Reply