Understanding the role of Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) is crucial for measuring stock market trends and investor sentiments. These institutions significantly influence market movements, liquidity, and overall stability.
In this blog we will discuss the Definitions, Types and Importance of FIIs and DIIs in Indian Stock Market. This blog of ours will help you understand the whole concept of FIIs and DIIs and take your Trading and Investing Journey to a more advanced level.
What is FII and DII?
FII (Foreign Institutional Investor):
Foreign Institutional Investors are investors or investment funds from outside a country that invest in that country’s securities market. They include large foreign financial institutions like mutual funds, pension funds, and insurance companies that invest significant amounts in financial markets.
Some examples of FIIs are: Government of Singapore, Goldman Sachs Funds, Fidelity Funds, Aidos India Fund Ltd, Nomura Singapore Limited Odi, Bao Value Fund.
DII (Domestic Institutional Investor):
Domestic Institutional Investors are investment entities within the country that invest in the country’s securities markets. DIIs include entities such as domestic mutual funds, insurance companies, banks, and other financial institutions.
Some examples of DIIs are: Tata Mutual Fund, Aditya Birla Sun Life Insurance Company Limited, Quant Mutual Fund, SBI Mutual Funds, Life Insurance Corporation of India (LICI).
Types of FIIs and DIIs
The following are diverse categories of domestic and foreign institutional investors in India:
Types of FIIs (Foreign Institutional Investors):
Hedge Funds: Private funds employ various strategies to achieve high returns for their investors.
Pension Funds: Large investment pools that provide retirement benefits through long-term investments.
Mutual Funds: Investment vehicles that collect money from numerous investors to buy a diversified portfolio of securities.
Investment Banks: Financial institutions that assist with capital raising, securities trading, managing mergers and acquisitions.
Insurance Companies: Firms offering risk management through insurance policies and investing collected premiums in financial markets.
Sovereign Wealth Funds: Government-owned investment funds that manage national reserves to achieve long-term financial stability.
Types of DIIs (Domestic Institutional Investors):
Indian Mutual Funds: Mutual funds collect money from individual Indian investors and invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, including Indian stocks. It allows individual investors to participate in the stock market even with small investment amounts.
Pension Funds: Domestic entities that manage retirement savings by investing in a range of asset classes to ensure long-term benefits for retirees.
Public Provident Fund (PPF): A government-backed long-term savings scheme in which individuals contribute regularly, earning tax-free returns and benefits upon retirement.
Indian Insurance Companies: These companies collect premiums from policyholders in India and invest a portion of those funds in Indian stocks and bonds. It offers long-term returns to policyholders while contributing to the growth of the Indian market.
Indian Banks: Banks collect deposits from individuals and businesses in India. They can invest a part of these deposits in Indian stocks and bonds for additional income.
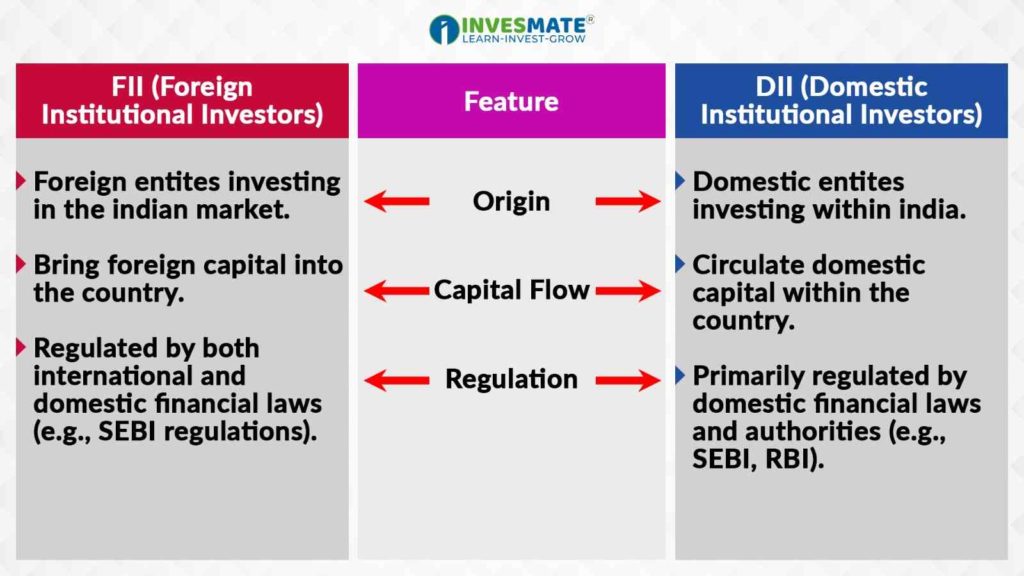
Difference Between FII and DII
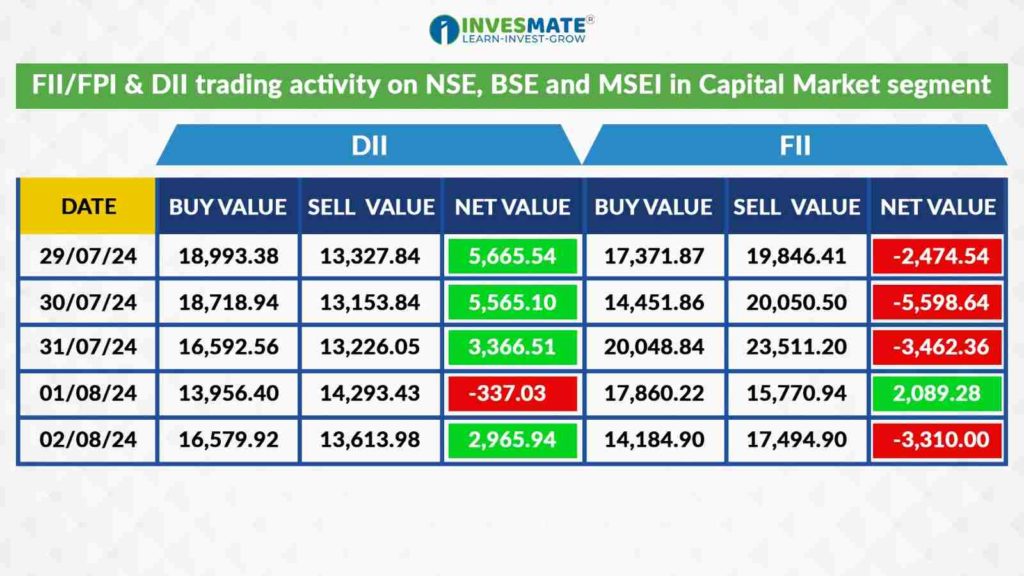
How to Analyse FII and DII Data Trading Activity?
- Net Inflows/Outflows: Check the net buying and selling figures to understand the market sentiment.
- Sectoral Investment: Analyse which sectors FIIs and DIIs are investing in to gauge sectoral trends.
- Volume: Look at the trading volumes to understand the impact on liquidity and market movement.
- Historical Trends: Compare current data with historical data to identify patterns and trends.
*Source: nseindia
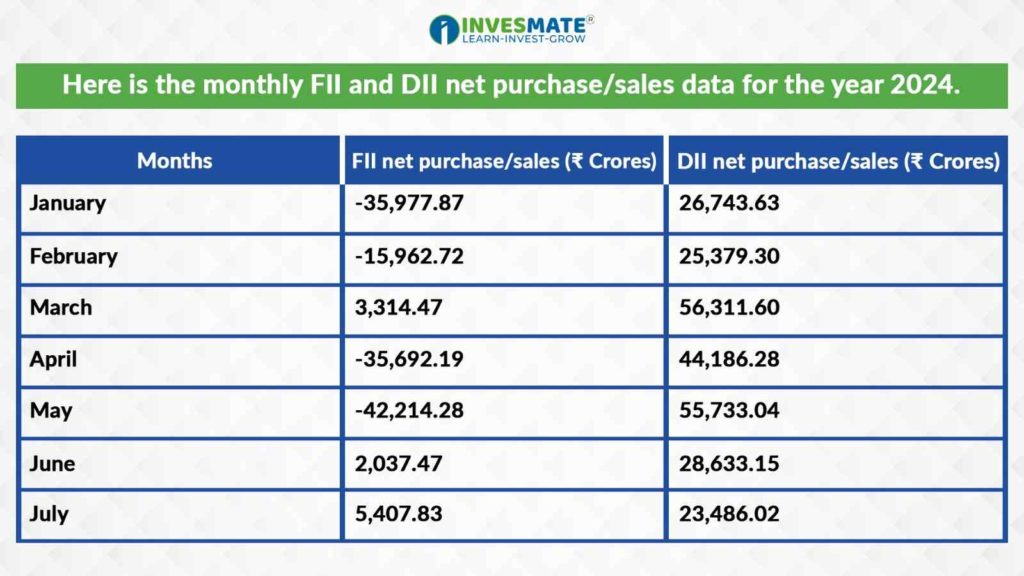
Here is the monthly FII and DII net purchase/sales data for the year 2024.
*Source: nseindia
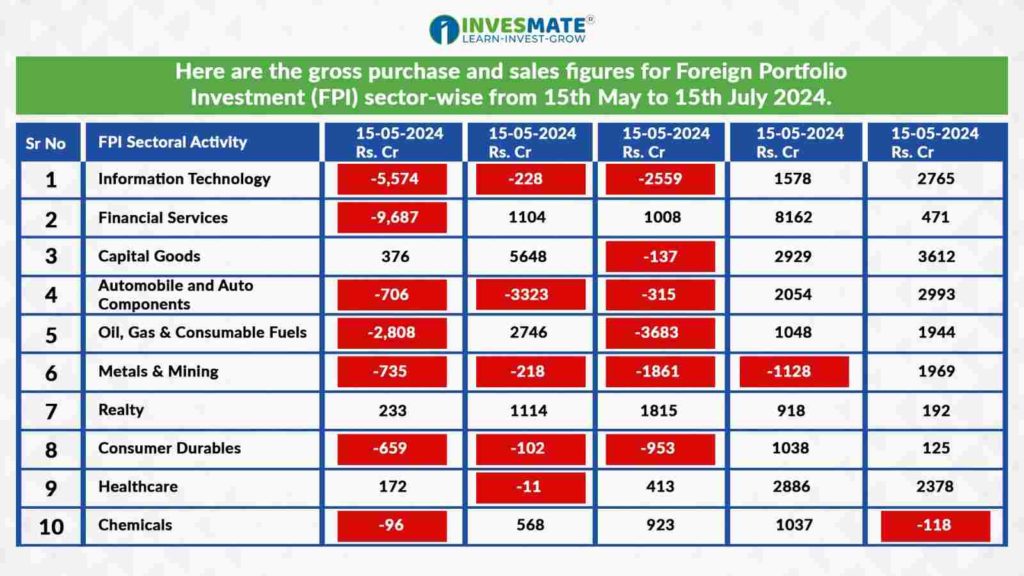
Here are the gross purchase and sales figures for Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) sector-wise from 15th May to 15th July 2024.
* Source: NSDL
Important Terms to Know in FII and DII Activity
- Net Investment: The difference between gross purchases and gross sales.
- Portfolio Investment: Investments in securities like stocks and bonds.
- FDI (Foreign Direct Investment): Direct investment in physical assets like factories, excluding portfolio investments.
- FPI (Foreign Portfolio Investment): Similar to FII, focusing on securities and financial assets.
FIIs and DIIs Impact on Stock Markets in India
- Market Liquidity: FIIs and DIIs provide liquidity to the market, making it easier to buy and sell securities.
- Market Trends: Their trading activity can influence market trends and investor sentiment.
- Economic Impact: FII inflows can indicate foreign confidence in the country’s economy, while DII activity reflects domestic investor sentiment.
Understanding FII and DII activity is crucial for investors in the Indian stock market. It provides valuable insights into market trends and economic sentiment through data analysis, helping both retail and institutional investors make informed decisions and establish their market positions.
FAQs
FII stands for Foreign Institutional Investor.
DII stands for Domestic Institutional Investor.
FIIs help develop hedging instruments, which can be used to manage risks and provide stability in the financial markets.
It provides analytical information on institutional investors’ behavior, which can be used to identify market trends and choose investments.
FIIs operate in India under the regulations set by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
FIIs are foreign entities investing in Indian stock markets, whereas DIIs are domestic entities. FIIs bring in foreign capital; DIIs use domestic capital.
এই তথ্য শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষামূলক উদ্দেশ্যে প্রদান করা হয়েছে। একে কোনোভাবেই Investment Advice বা Recommendation হিসেবে গণ্য করা উচিত নয়। আমরা একটি SEBI-registered Organization, এবং আমাদের মূল লক্ষ্য হলো বিনিয়োগ সম্পর্কিত Concepts-এর সাধারণ জ্ঞান ও বোঝাপড়া বৃদ্ধি করা।
প্রত্যেক পাঠক/দর্শককে অনুরোধ করা হচ্ছে, যেকোনো Investment Decision নেওয়ার আগে নিজস্ব Research এবং Analysis করুন। Investment সর্বদা হওয়া উচিত ব্যক্তিগত Conviction-এর ভিত্তিতে, অন্যের মতামত থেকে নয়। অতএব, প্রদত্ত তথ্যের ওপর ভিত্তি করে নেওয়া কোনো ধরনের Investment Decision-এর জন্য আমরা কোনোভাবেই Liability বা Responsibility গ্রহণ করি না।



Leave a Reply