What is a Commodity?
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold. They are usually standardized and interchangeable with other goods of the same type, allowing them to be traded on exchanges.
History of Commodity Trading
Commodities trading has a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations where goods like grains, spices, and metals were exchanged. Modern commodities trading began to take shape with the establishment of organized exchanges in the 19th century.

Types of Commodities
Commodities can be categorized into four main groups :
Energy :
This segment includes crude oil and natural gas.
Base metals :
This segment includes crude oil and natural gas.
Bullion :
Gold & Silver.
Agricultural commodities :
Cardamom, rubber, mentha oil, palmolein, castor seed, black pepper, cotton are included in this segment.
Gold, corn, crude oil, brent, silver, wheat and coffee are a few of those most traded commodities across the globe.
Price movements in a commodity in one part of the world tend to have a ripple effect on the commodity in other geographies.
Future contracts in Commodities
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a commodity at a predetermined price on a specified date. They provide investors with a way to speculate on the price movements of commodities without owning the physical asset.
Livestock and Meat
Livestock commodities include cattle, hogs, and poultry. Meat commodities include beef, pork, and poultry products.
Stocks to Invest in Commodities
- Try to Invest in companies that are involved in commodity production, exploration, or distribution.
- Gain exposure to commodity price movements indirectly through stock performance.
- Stock Example: Coal India, Hindustan Zinc, Adani Green Energy etc.
ETFs and Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) to Invest in Commodities :
Exchange-traded note (ETN)
An exchange-traded note (ETN) is an unsecured debt security that tracks an underlying index of securities. ETNs are similar to bonds but do not pay periodic interest payments.
ETNs do not provide investors ownership of the securities but are merely paid the return that the index produces.
exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are different from ETNs. ETFs own the securities in the index they track. For example, an ETF that tracks the S&P 500 will own all 500 stocks in the S&P. When you invest in an ETF, you are investing in a fund that buys and holds shares of the assets in the benchmark it tracks.
What Are Commodity Mutual Funds?
A commodity fund is a type of mutual fund that invests in commodities such as gold, silver and real estate that offer capital appreciation and a hedge against inflation.
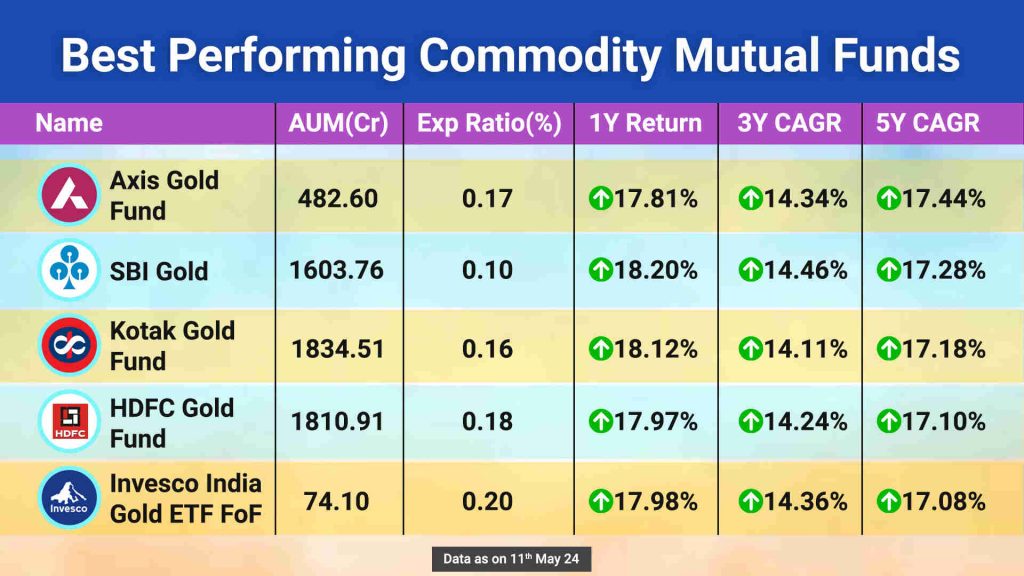
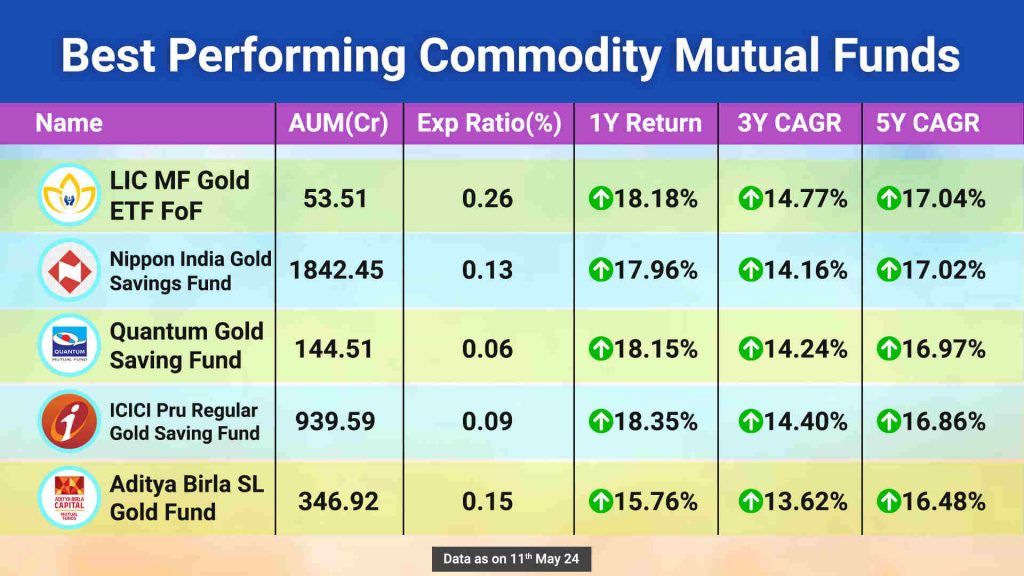
Commodity mutual funds invest in commodities and are frequently structured in one of three ways :
▸ Equity holdings in commodity-related companies
Commodity mutual funds will hold equities in commodity-related companies such as those of agricultural, energy or mining companies.
▸ Futures-based funds
The second structure for commodity mutual funds is futures contracts. These trade on exchanges, similar to stocks and bonds, and don’t require storage like a physical commodity does.
When a futures contract approaches the delivery date, the contract holder will typically “roll” that contract in exchange for another contract of the same commodity to be delivered further in the future.
▸ Combination of equities and futures
Finally, some funds will hold a combination of both equities of commodity-related companies and commodities futures contracts.
How To Invest in Commodity Markets
Investors can trade commodities through futures contracts, options, ETFs, and mutual funds. Each method has its own advantages and risks, so investors should choose the approach as per their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Pros and cons of commodity trading
Pros :
- Diversification: Low correlation with traditional assets aids portfolio diversification.
- Inflation hedge: Acts as a hedge against rising prices during inflationary periods.
- Potential for high returns: Offers significant profit opportunities due to market volatility.
Cons :
- Volatility: High volatility in the market can lead to substantial price swings and potential losses.
- Speculative risks: Involves unpredictable speculation on future price movements.
- Storage and transportation costs: Additional expenses for physical commodity investment.
FAQs
The main types of commodities are agricultural, energy, metals, and livestock.
Future contracts are agreements to buy or sell commodities at a predetermined price and date, enabling speculation on price movements.
Livestock and meat commodities include cattle, hogs, beef, pork, and poultry products.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Exchange-Traded Note (ETNs) track commodity performance, providing convenient investment without futures trading.
Methods for investing in commodity markets include future contract, options, ETFs, and mutual funds.
এই তথ্য শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষামূলক উদ্দেশ্যে প্রদান করা হয়েছে। একে কোনোভাবেই Investment Advice বা Recommendation হিসেবে গণ্য করা উচিত নয়। আমরা একটি SEBI-registered Organization, এবং আমাদের মূল লক্ষ্য হলো বিনিয়োগ সম্পর্কিত Concepts-এর সাধারণ জ্ঞান ও বোঝাপড়া বৃদ্ধি করা।
প্রত্যেক পাঠক/দর্শককে অনুরোধ করা হচ্ছে, যেকোনো Investment Decision নেওয়ার আগে নিজস্ব Research এবং Analysis করুন। Investment সর্বদা হওয়া উচিত ব্যক্তিগত Conviction-এর ভিত্তিতে, অন্যের মতামত থেকে নয়। অতএব, প্রদত্ত তথ্যের ওপর ভিত্তি করে নেওয়া কোনো ধরনের Investment Decision-এর জন্য আমরা কোনোভাবেই Liability বা Responsibility গ্রহণ করি না।



Leave a Reply